In today’s complex and rapidly evolving rail shipping industry, understanding the financial performance of railroads and its implications on businesses is crucial for making informed decisions and optimizing operations. The industry’s capacity to provide reliable, cost-effective, and environmentally conscious transportation services hinges on its ability to adapt to market trends and respond to challenges that emerge.
The third quarter of 2023’s results present a unique opportunity to examine the current status of the industry and the specific factors that contribute to its ongoing development. To better equip professionals in the rail shipping industry with the knowledge and tools necessary for navigating these complex waters, this comprehensive analysis delves into the railway’s financial performance, exploring rail rates insights, strategies for rate negotiations, and leveraging data insights for more informed decision-making.
A Detailed Study of Railways’ 3rd Quarter 2023 Results
The railways’ financial performance in the third quarter of 2023 sheds light on the economic issues in the industry. Looking closer, we can see a concerning mix of falling income, rising expenses, and dropping volume. This presents a difficult challenge for the railroads, who will try to compensate by raising rates to make up the difference in income.
Revenue Down, Costs Up, Volume Down
The railroad’s 2023 third quarter results show a decrease in revenue, an increase in costs, and a decrease in volume.
The largest railroads are all showing a year over year decrease in revenue from 2022. For instance, compared to third quarter 2022, the Norfolk Southern reported an 11% drop in railway operating revenues, while the Union Pacific reported a drop of 10%.
Part of the decrease in revenue is because of a drop in volume for some of the Class I railroads. For instance, Union Pacific reported business volumes, as measured by total revenue carloads, were down 3%.
The drop in revenue and volume can be attributed to a few factors, including inflationary pressures, fears of an upcoming economic downturn, and service issues. The Eastern Ohio Incident has also continued to have lasting effects on some railroad’s revenue, as shippers consider possible alternate methods of transportation.
At the same time, an increase in expenses is a challenging barrier to achieving financial efficiency and profits for the rail shipping industry. Higher operation costs, often connected to changing commodity prices, investment in infrastructure, or labor costs, unavoidably affect the final profit. Most recently, rising fuel and manpower costs have both contributed to the railroads showing an increase in their operation costs.
The Coming Increase in Rates
The combination of a decrease in revenue and volume, and an increase in operating costs, paints a clear picture: rates are likely to increase. With the third quarter results as our source of data, we believe that rail rates will continue to rise as the railroads try and offset the higher operating costs and lower volumes.
Understanding the Effects of Financial Troubles on Railroad’s Operating Ratio
In the rail industry, the term Operating Ratio is used in relation to the railroads. What is the Operating Ratio? Put simply, it is Costs divided by Revenue. It’s a key element that can be used to measure profitability and efficiency and makes for a great comparison tool when looking at the railroad’s performance. Anyone working in the rail shipping industry, shipping by rail for their business, or just paying attention to economic contributors, are keeping an eye on the Operating Ratio of the railroads for a multitude of reasons. And the railroads are constantly seeking to improve their Operating Ratio by finding ways to reduce costs and boost revenue.
Given the recent third quarter reports of increasing expenses and dropping revenue, the rail shipping industry faces a big challenge: the Operating Ratio is bound to get higher. This forces the railroads to take combined steps specifically aimed at lessening or halting this increasing trend.
Operating Ratio: A Number Watched Closely
It’s worth repeating that not only the railroads keep a close watch on the Operating Ratio. Wall Street, where investment choices are made based on a company’s financial health, also scrutinizes it. This stresses the significance of making strategic choices and carefully balancing revenue and cost.
Industry professionals need to create shifting action plans based on data analysis to make real improvements in their operations. By doing this, they arm their companies with the knowledge and tools to adjust to the changing environment, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and profitable way of doing business.
The Railroad’s Possible Response
With the railroad’s recent financial reports hitting the rail shipping industry, it’s expected that rail rates will increase to help mitigate the downward trend. This isn’t unexpected; rail rates were already trending up even before the recent quarter’s results. This consistent upward trend is seen as a strategic reaction to the problems the industry is currently facing, and part of the attempt to improve the Operating Ratio.
It’s important for professionals involved in the industry to recognize this trend is a natural part of how the rail industry works. Furthermore, if your business is affected by rising rail rates, it’s important to have a deep understanding of how the railroads price. This understanding can be a powerful tool during contract discussions, potentially reducing overall rail cost and rail spend.
The Structure of Rail Pricing
Rail pricing uses a unique strategy, similar to the mark-up used by retailers. Railroads add to their costs using commodity-specific Revenue-to-Variable Cost (RVC) ratios. The RVC is the inverse of the Operating Ratio and is calculated by dividing Revenue by Cost. However, unlike the Operating Ratio, the RVC is calculated on an individual lane basis. Understanding this pricing model is crucial when looking to reduce costs and plan financial strategies.
Effect of RVCs on Operating Ratio
An increase in these RVCs impacts the Operating Ratio, driving it downwards. As a result, it’s a common strategy the railroads use in times of high Operating Ratios.
Addressing Lack of Volume by Increasing Carloads
An alternative approach railroads can take to address falling volumes is increasing carloads.
One method they could use to accomplish this is by going after business opportunities that are currently moving adversely to them, to increase their overall volume. It is, however, crucial for railroads to be careful utilizing this strategy. If they are not cautious, they could start a pricing war with competitors, which could paradoxically increase costs while reducing volume.
Additional new volumes can also be created by changing the transport mode that businesses use. For example, some railroads are currently focused on establishing cross-docking operations involving boxcars. Their intent is to make it easier to implement rail shipping for all, or part, of a business’ supply chain networks, to persuade a change from another mode of transportation, like truck, to rail.
Handling Contract Discussions and Tariffs Successfully at Year-End
The last months of the financial year are critical for businesses who ship by rail. Particularly, many contract discussions take place at year-end. These talks between railway operators and their clients help shape business plans for the next year and give an idea of what it will cost to ship by rail. So, it is important to be well-prepared and understand thoroughly what is needed for these discussions.
The Importance of Preparation
Being well-prepared for these discussions is key and a carefully planned strategy can change your negotiation results, potentially producing better results. Good preparation is based on understanding fully the current financial situation, supported by a clear picture of market trends. Using solid data and useful insights, negotiators can navigate through the intricacies of railway tariffs and finalize a contract that meets their terms best.
Strategic Steps in Negotiation Process
The negotiation process can be handled strategically using several key actions:
- Put forth a well-grounded suggestion for a lower rate, based on a detailed understanding of the rail operator’s pricing strategy. This step relies on understanding how the railway adds to its costs, the specific Revenue to Variable Cost ratios for the railway, and their effect on rate setting.
- Identify and aim for specific rates if they are unusually high, what we call ‘out-of-line’. To pinpoint these exceptions requires rigorous data study and clear communication with the rail operator.
- Strive to lower the proposed rate hikes for specific lanes in contracts instead of trying to reduce the raise across all lanes. This approach allows for more focused negotiation tactics and leads to better results due to the targeted nature of the strategy.
Understanding Railroad Costs and Revenues
In the rail shipping industry, smart choices and successful discussions depend on understanding the costs and standard revenues of individual shipping lanes thoroughly. By deeply analyzing these elements, one can detect unusually high rates, discover negotiation strengths, and focus efforts on lanes that have the greatest potential.
A. Spotting Unusual Rates
Finding rates that are significantly different from common industry rates requires close examination of revenues and costs across different lanes. Spotting these rates opens opportunities for saving costs and planning focused negotiation strategies, especially ones aimed at fairness. Besides, knowing about these unusual rates helps rail professionals concentrate their efforts on fixing these financial imbalances.
B. Identifying Negotiation Strengths
Negotiation strengths refer to the power one has compared to the other party during discussions. Through a detailed study of costs and revenues for different lanes, rail professionals can identify where they have a strong bargaining position. Knowing these areas empowers negotiators to strategically obtain better conditions, leading to overall enhanced results.
C. Concentrating on Specific Lanes for Negotiation
With a broad understanding of costs and revenues specific to each lane, industry professionals can smartly identify lanes that offer the best negotiation opportunities. Focusing on these particular lanes allows negotiators to maximize cost savings and revenue increases by concentrating their efforts on lanes that have either unusual rates, high negotiation power, or both.
D. Handling Rate Increase Discussions
During negotiations, the chance of rate increases is often important for both parties. Rail professionals are advised to handle these proposed increases with a data-led, planned approach. In some cases, accepting reasonable rate increases on select lanes could be justified if market dynamics and cost changes demand it. On the other hand, if rates are already high, efforts should be made to reduce unnecessary financial load.
Leveraging Rail Impact for Insights and Data Accessibility
In the data-driven arena of the rail shipping industry, our Rail Impact® platform offers features specifically designed to enhance your ability to negotiate your rail rates.
A. Proprietary Cost Model
Understanding the cost infrastructure of railroad operations is fundamental. Rail Impact’s proprietary cost model provides a distinctive lens to help professionals unearth the layered complexities and decipher the railroad’s cost structure effectively. This purpose-built model unfolds the financial intricacies and informs decision-making significantly.
B. Proprietary Benchmarks
Accuracy and specificity in data analytics are powerful. Rail Impact leverages proprietary benchmarks that are both lane-specific and commodity/car type specific. This precision enables users to craft targeted, data-informed strategies pertaining to individualized shipping lanes and specific commodity/car types.
C. Market Data
Trends drive progress. Rail Impact offers a robust assembly of market data to scrutinize trends and evaluate traffic flows by commodities. This time-based scrutiny of market trends offers an empirical understanding of not only the current status quo but also the propensity toward future trajectories.
D. Reference Information
Knowledge is power. Complementing the above, Rail Impact also provides a wealth of reference information. This includes a Fuel Surcharge Table, the Serving Carrier/Reciprocal Switch (SCRS) database, and a series of comprehensive rail directories. These resources serve as invaluable tools aiding professionals in establishing a well-rounded understanding of the rail shipping industry dynamics.
The rail shipping industry is continuously faced with challenges and opportunities that arise from market trends, economic forces, and evolving business models. This in-depth analysis of the third quarter 2023’s railroad financial results highlighted several key areas of concern and potential strategies to address them, with a focus on understanding revenue dynamics, cost structures, and volume changes.
By closely monitoring the industry’s financial performance and leveraging advanced data analytics tools like Rail Impact®, professionals can develop more informed, data-driven strategies for negotiation, cost-saving, and revenue optimization.
In the face of rising rates, falling volumes, and economic uncertainties, a comprehensive understanding of the industry’s financial landscape empowers rail professionals to make well-informed decisions, cultivate resilience, and ultimately lead their businesses towards long-term success in the ever-changing rail shipping industry.







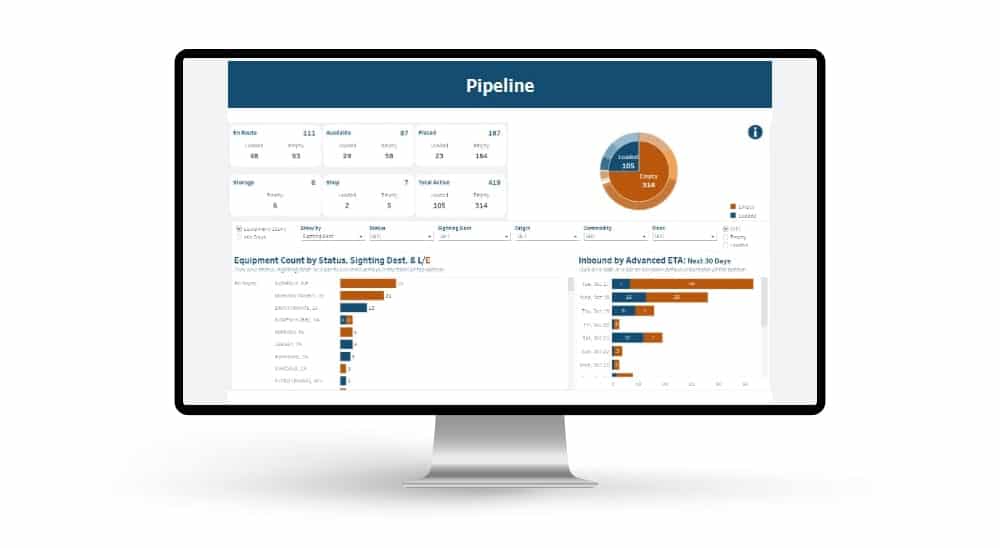 Automated exception reporting of the railcar tracking data makes it easy to identify and troubleshoot jeopardized shipments, thereby enabling you to provide better service to your stakeholders.
Automated exception reporting of the railcar tracking data makes it easy to identify and troubleshoot jeopardized shipments, thereby enabling you to provide better service to your stakeholders.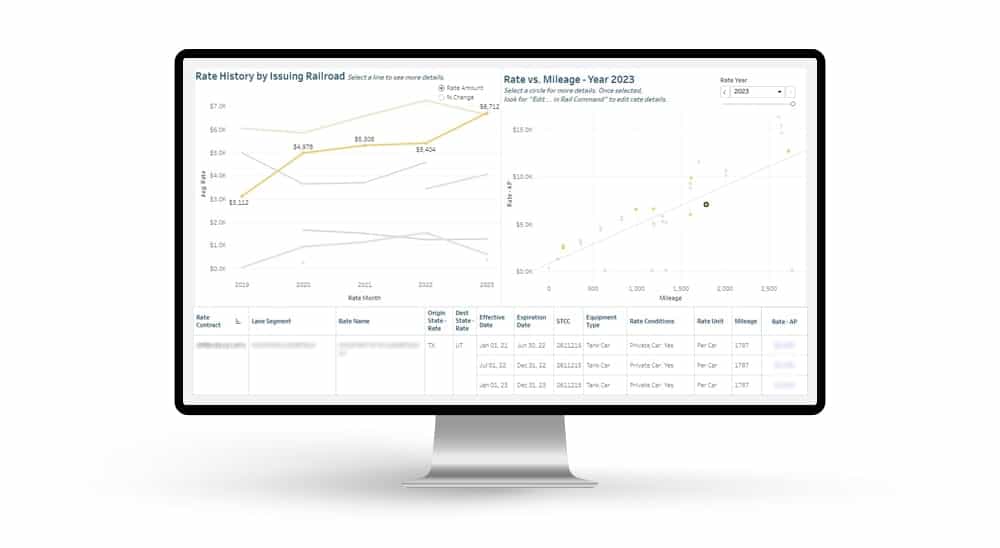 Receive notification of pending rate expirations. Tariff changes and fuel surcharges can be automatically updated.
Receive notification of pending rate expirations. Tariff changes and fuel surcharges can be automatically updated.