Freight transportation forms the backbone of North American commerce, ensuring the efficient movement of goods across diverse market sectors. In this vast network, rail systems play an important role, since their high capacity and long-haul capabilities offer one of the most effective modes of freight transportation. However, the increasing demands of modern logistics necessitate enhanced efficiency, bringing us to the advent of rail automation.
The concept of rail automation involves the use of automated systems to streamline rail operations. The goal of these automated solutions is significant improvements in speed, precision, and overall operational reliability. As rail automation continues to evolve, it opens new possibilities in freight transportation, making it a crucial focus area for the industry’s future development.
Evolution of Rail Freight Transportation
Rail freight transportation has played a pivotal role in North America’s logistical infrastructure since the inception of railroads. The capacity to shift massive quantities of freight across extensive distances solidified rail transport as a key element in the continental distribution system, dominating until the rise of freight trucking and aircraft.
Over time, railroads have undergone significant transformations. One primary example of the changes the industry has gone through in only a couple hundred years is the upgrade from steam engines to fuel-propelled locomotives, and presently to electric locomotives. Rail freight transportation has advanced as well, and now positions a variety of specialized and generic railcars to cater to diverse freight types.
Safety and security provisions have also been strengthened in modern railroads, and the integration of technology is continuously adopted within the rail shipping industry. This progressive adaptation streamlines the functions of railroads and rail shippers, fostering consistent growth and improvement of rail transportation.
The Shift Towards Rail Automation
In response to the demands of an expanding population and industrial growth, the scale of freight rail has surged. Contemporary statistics illuminate this trend; in 2021, for instance, the length of a freight train on a Class I railroad extended to a median of 5,400 feet. This growth of goods and railcars means larger rail yards are required to facilitate the assembly of longer trains, particularly when accommodating specialized cargo with unique handling and safety requirements.
Heightened complexities in rail operations – including the escalation of monitoring and executing freight shipping – means that rail logistics management and rail rate analysis are becoming increasingly intricate, evolving into full-time operational roles.
As rail freight shipping becomes more multifaceted, the industry must invest additional resources to ensure that shipments are efficiently organized, routed, and executed. Core logistics tasks such as rate management, railcar tracking, demurrage dispute resolution, shipment execution, and more, are becoming more resource intensive. Beyond these, logistics management often extends to overseeing a multitude of railcars within crowded yards or entire fleet management duties. Investment in time, effort, and financial resources is substantial, and the need for more efficient processes has never been more pressing.
Enter the era of rail automation.
Automation excels in executing tasks with accelerated speed and pinpoint accuracy, while being free from the pitfalls of human error. For the increasingly complex landscape of rail shipping, loaded with the burdens of manual involvement, automation promises a revolution. It’s not merely about superseding manual tasks; automation opens new horizons for strategic optimization, yielding time and cost savings while mitigating the risks of human oversight.
Overview of Rail Automation Tools
The more demand grows in the rail shipping industry, the more complex its operations grow. In response, cutting-edge solutions that utilize automation are making operational tasks smoother and easier to manage. These innovations cover a wide spectrum, from yard management systems optimized to refine the coordination of railcars and freight, to rail logistics management platforms that address a broad spectrum of logistical tasks.
Advanced yard management tools like Yard Manager use automation to make operations within rail yards run more efficiently. Automation is primarily used to help improve the order and flow of railcars and freight. This leads to drastically reduced dwell times while simultaneously boosting throughput, significantly improving overall operations.
Another area is rail logistics management platforms, which cover a wide range of tasks. An excellent example of this is Rail Command®, a software that combines useful tracking systems with cutting-edge automation technologies. This makes managing the different facets of rail shipping operations more efficient, from precise tracking of railcars, effective management of logistical components, handling of diversion requests, and generation of comprehensive reports. As a result, these tools save a lot of time and money while improving strategic flexibility in rail shipping operations.
Finally, rail rate analysis solutions such as Rail Impact® are also leveraging automation to simplify confusing rate structures. By providing a clear breakdown and visibility of rail rates, businesses can negotiate better deals, improving the financial outcomes of rail shipping.
Yard Management: Automating Railyards
Yard management applications are designed to optimize operations within rail yards by automating the activities of railcars within the rail yard and making it simpler to track their movements from entrance to exit. These applications create a digital “twin” of the railyard, allowing for real-time railcar lifecycle tracking, including arrival, inspection, cleaning, repairs, loading, billing out, and departure. The primary goal of yard management solutions is to increase the visibility and efficiency of railyard operations.
Let’s use the Yard Manager application as an example of a yard management solution and its uses.
Manage Rail Yards
The key to managing railyards effectively is the integration of automation in inputting railcar identifiers. For instance, Yard Manager transposes Automated Equipment Identification (AEI) reader data into digital formats, mirroring the functionality of sensor data. This integration ensures every railcar’s journey through the yard is meticulously monitored and recorded, enhancing the accuracy of yard management.
Increase Efficiency and Organization
Yard Manager’s features such as Car Flow, Inventory Summary, Regional Visual Yard View, Railcar Records, Switch Plan Creation, and Sequential Asset Lineup offer a comprehensive suite of tools geared towards maximizing efficiency and organization. By automating train manifest data processing, the system reduces manual entry, leading to more accurate and more efficient entries. This automation, along with demurrage and customer holding cost reduction features, streamlines operations, and upholds financial integrity.
Rail Management: Streamlining Rail Logistics
Rail management solutions are essential for simplifying the complexities of rail logistics through a cohesive suite of automated tools. These tools, which cover everything from comprehensive shipment tracking to fleet management and freight processing details, are designed to boost operational efficiency, ease of use, and accurate data reporting. Integrated solutions, which combine multiple tools to create a seamless operational flow, are particularly effective as they allow for the automation of a wider array of tasks and more comprehensive problem-solving.
A prime example to use when talking about automated, integrated rail management solutions is Rail Command®. This comprehensive software platform is developed for complete oversight of rail logistics. It consolidates functionalities such as railcar tracking, demurrage management, and automated reporting into one connected solution.
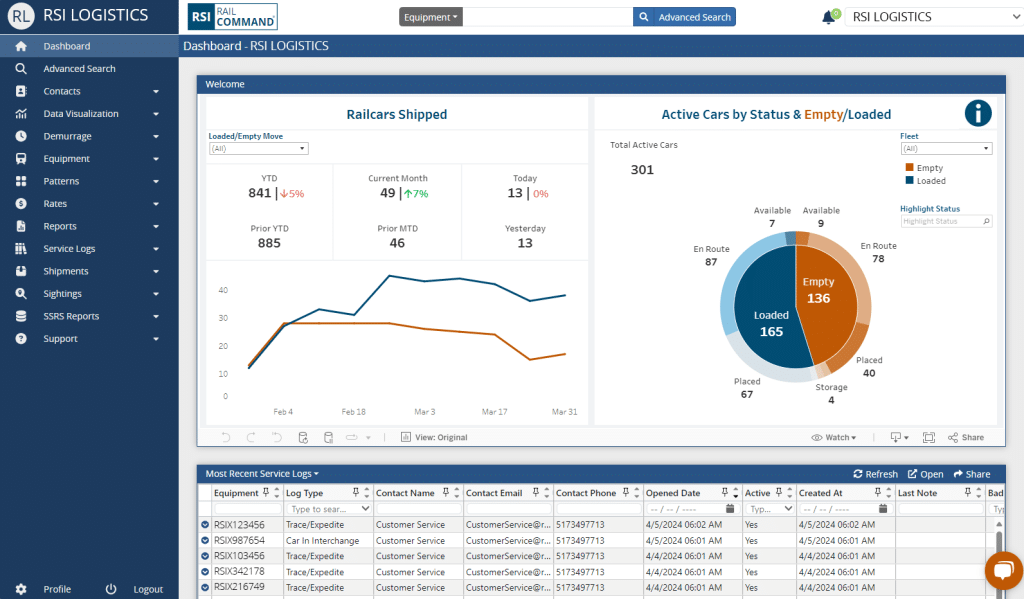
Let’s look at what rail automation is in rail logistics management solutions.
Automated Tracking and Tracing
An important aspect of any rail logistics automation is the ability to track and trace railcars. Accurate, automated tracking allows you to more easily view where your railcars are, and saves time spent manually searching for them. This tracking can utilize different methods. For instance, Rail Command® enables shippers and receivers to track railcars throughout North America using a continuously updated Car Location Messages (CLM) feed. The system also automates alerts about potentially delayed or problematic railcars, enabling proactive measures to alleviate situations before they escalate.
Automated Demurrage Management
Rail management solutions like Rail Command® help alleviate demurrage charges by making it easy to monitor how long railcars have been at a location. The platform analyzes how long railcars have been stationed and calculates the associated demurrage charges. This allows you to easily monitor railcars, track accruing charges, and generate data-driven disputes when necessary. Automation can also provide invoice-ready reports, simplifying the process and assisting in maintaining cost discipline throughout operations.
Automated Rate Management
Automated rail rate control is important for the ability to track contracts, tariffs, and fuel charges. Automation of rail rates in tools such as Rail Command® includes notification of pending rate expirations, while fuel surcharges can be automatically updated . Another resource that is important is an automated Fuel Surcharge calculator for rates tied to patterns.
Automated Data Visualization
An important aspect of rail management solutions is the ability to view data generated from rail logistics activities. For instance, Rail Command® comes standard with a plethora of data visualization Key Performance Indicator (KPI) reporting and a grid view customer report builder.
Automated Fleet Management
Whether you’re a rail shipper who leases railcars or manages a fleet, automation is important to ensure you can manage both. Automation in tools like Rail Command® allows you to track and manage lease agreements, as well as manage cars in your fleet as they go to and from shops.
Automated Freight Audit
Some automated rail management solutions, like Rail Command®, can automatically audit freight bills executed out of their systems.
Rail Rate Analysis: More Effective Negotiations
The meticulous scrutiny and maintenance of freight shipping rates is essential for making strategic decisions regarding competitive pricing, budgeting, and financial planning – all key components in negotiating rates with railroads. Its complexities lie in handling multiple rate structures, contracts, tariffs, and fuel surcharge iterations.
Automating this process removes a large amount of manual labor, which in turn saves time, as well as removes the possibility for human error. We’ll use the Rail Impact® rail rate analysis tool as an example for rail rate analysis automation.
Rail rate analysis tools like Rail Impact® equip you with robust automation for managing the preparation of rail rates for negotiations. These tools are designed to deliver precise, comprehensive oversight of rail rates, offering insights into rail freight rates relative to the market, fuel surcharges, and routing costs.
Rail Rate Database
Tools like Rail Impact® include a secure database to detail, access, and analyze freight lanes, serving carrier identification, individual rail segment analysis, and rail cost benchmarking. Additionally, automation can make it easy to search for alternative routing options, rail mileages calculation, and quick access to rail-related information, which all contribute to simplifying the rate management process.
Negotiation
For rail rate negotiations with rail roads, Rail Impact® is equipped with a proprietary cost model, complementing the government’s Uniform Rail Costing System (URCS), updated with quarterly railroad financial data. This information automates insights into vendor costs, aiding in rate target development and anticipation of rail rates without awaiting a quote. This insight, combined with the analysis of your rates against the wider market and profitability comparisons, offers a strategic advantage in negotiation dealings.
The evolution of the rail shipping industry towards high-tech, automated solutions is a timely and imperative shift. Encompassing efficient yard management, seamless logistics, and strategic rate analysis, these innovative tools are not just enhancing operations – they’re transforming them.
As they continue to evolve, these solutions will further streamline processes, introduce cost and time savings, and support better strategic flexibility. For those in the freight transportation sector, embracing these developments is more than an option – it’s a necessity for future success. Stay on track by leveraging these advancements, pioneering the future of rail shipping operations.
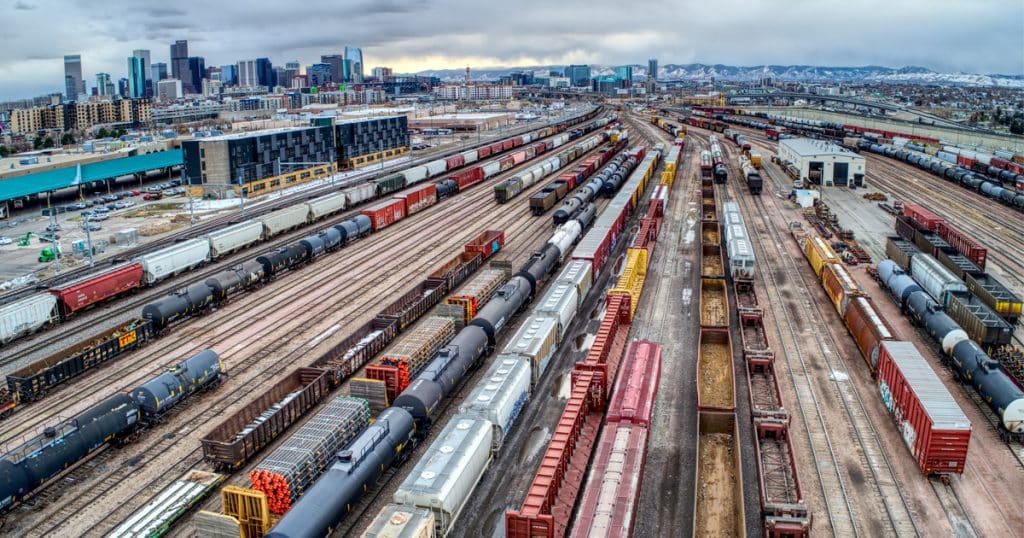
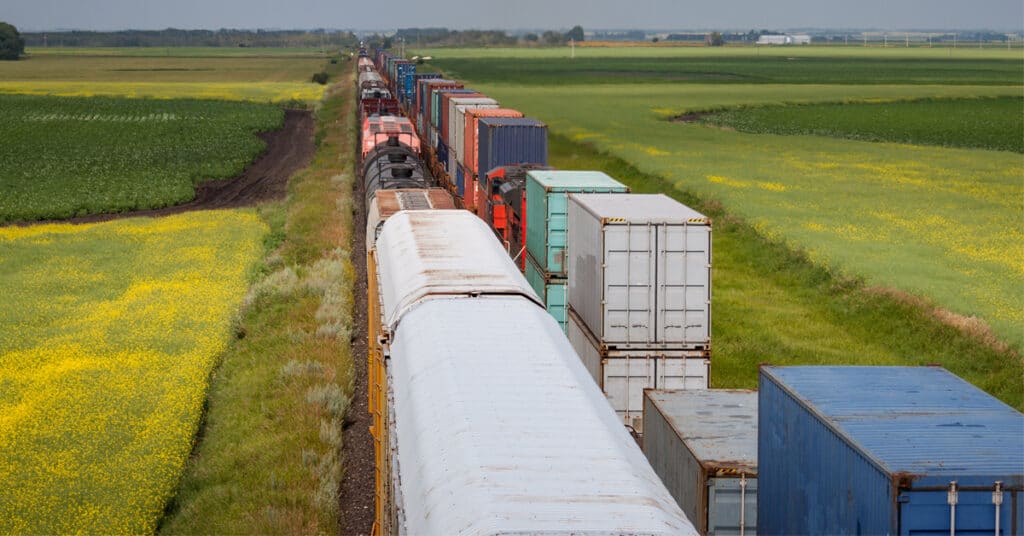
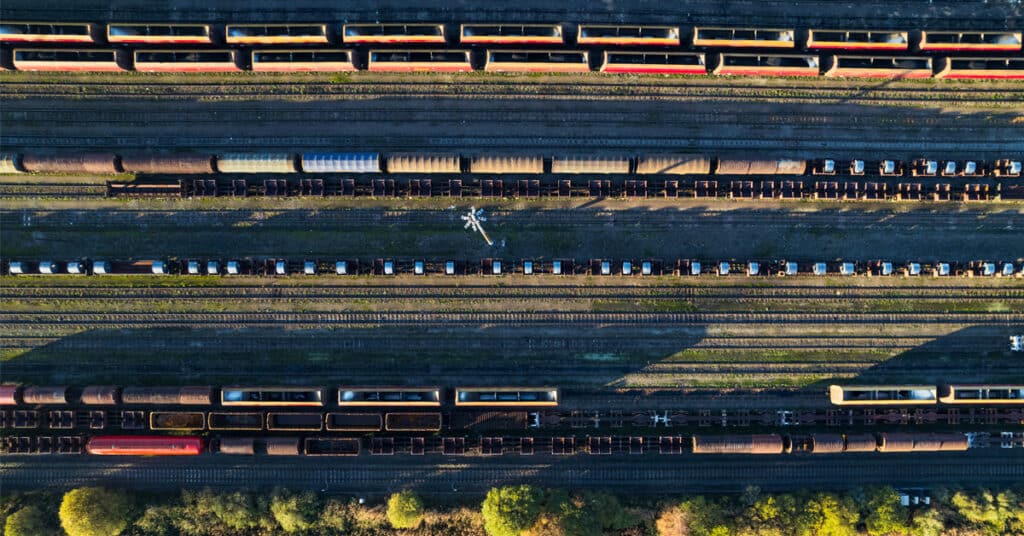



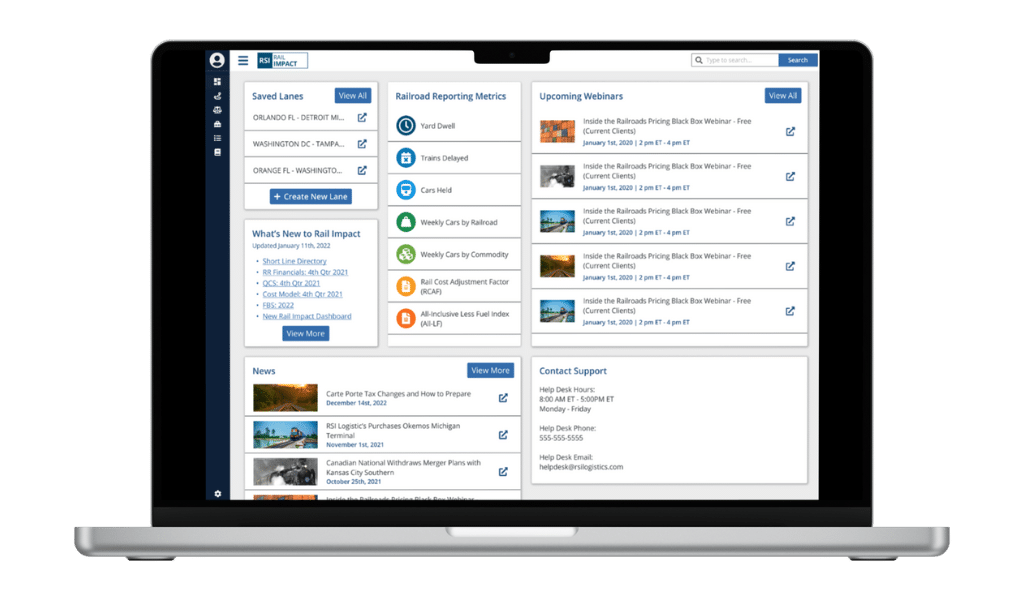


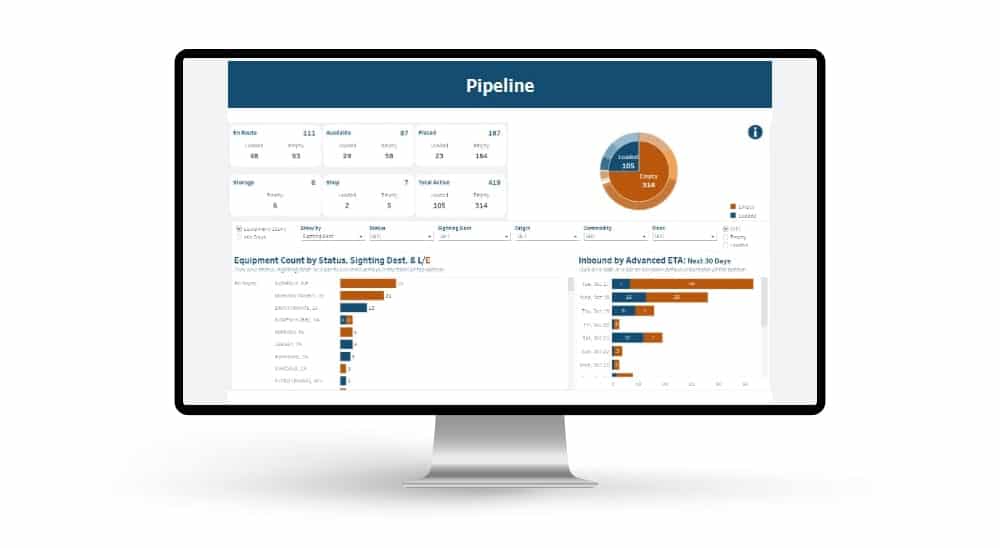 Automated exception reporting of the railcar tracking data makes it easy to identify and troubleshoot jeopardized shipments, thereby enabling you to provide better service to your stakeholders.
Automated exception reporting of the railcar tracking data makes it easy to identify and troubleshoot jeopardized shipments, thereby enabling you to provide better service to your stakeholders.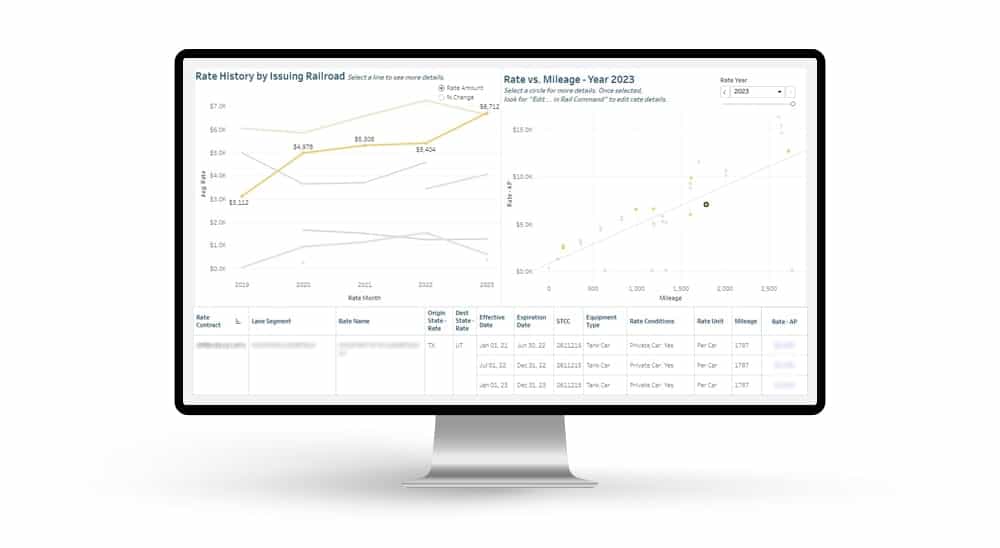 Receive notification of pending rate expirations. Tariff changes and fuel surcharges can be automatically updated.
Receive notification of pending rate expirations. Tariff changes and fuel surcharges can be automatically updated.