Shipping hazardous materials can be dangerous and can have serious consequences when done incorrectly. When shipping hazardous materials by rail, safety and compliance measures help to mitigate these risks, and mitigate harm if an incident occurs. Knowing and understanding these safety and compliance measures for shipping hazardous materials by rail will help to prevent delays, fines, and harm to workers and the environment.
Critical Regulations for Shipping Hazardous Materials by Rail
For shipping hazardous materials, the most frequently cited safety violations arise from Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) Title 49 CFR Parts 100-185. These regulations detail how hazardous materials must be documented and secured when shipped by any mode, including pipelines, highways, waterways, air, and rail. The Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) issues the HMR, while other relevant authorities enforce it. For hazardous material rail shipping, the Federal Railroad Administration is responsible for inspections and enforcement of the HMR.
These laws are in place to protect workers, the public, and the environment from the potential health risks of hazardous materials. Compliance with the HMR is required by law. All shippers of hazardous materials are responsible for understanding and complying with these regulations. Noncompliance can result in delays and fines, and deliberate noncompliance can result in criminal prosecution, especially if harm results from a lack of proper safety or documentation procedures.
Proper Training
Proper training is the first line of defense against hazardous material risks. Training personnel on how to secure hazardous material tanks on railcars and how to properly fill out and deliver documentation can help to reduce issues down the line. RSI uses detailed training materials and instruction to ensure all staff members understand securement and documentation procedures.
When conducting training, the following can be especially helpful:
- A visible, easy-to-follow guide or checklist explaining safety or documentation procedures. This guide or checklist should be readily accessible either in a paper or electronic format.
- Instruction from an expert. Seeing how the process is done, understanding common mistakes that can be made, and understanding why these procedures are important all help to increase compliance.
- Hands-on training with an expert. Trainees should go through the procedures themselves, under the supervision of an expert.
- Verification by an expert. A second look is always useful to ensure the job is finished properly, especially when that person has experience with the task.
Consistent and Uniform Securement
The railcar tank carrying hazardous materials must be properly secured when it leaves the shipper, and at every exchange point throughout the journey. When a railcar tank is properly inspected and secured from the outset at the shipper’s location, issues with inspections are much less likely later on.
Colored seals linked through or around bolts, chains, pins, and other components show that at-risk areas of the tank car are secured. This also prevents tampering with the tank. Improperly placed tags, such as those placed around unsecured plugs or open valves can create problems. Proper training, detailed documentation and verification can help to prevent this.
For non-pressure rail cars, leaks most commonly occur at the following areas:
- Manway gasket and cover
- Flanged and bolted connections
- Threaded connections
Tool-Tight Securement
Proper tools must be used to secure vulnerable components on the car. Manually checking or tightening valves and bolts is not enough. Nuts, bolts, caps and valves must be tightened with the proper tool. Remember that railcars endure a lot of vibration as they move, and this vibration can dislodge fittings that appear secure at first glance. Upon inspection, if fittings are found to be less than tool-tight, these areas will be marked.
Securement Documentation
Documenting the securement process not only helps to ensure that all procedures are followed, but also helps to prove that these procedures were conducted. A Railcar Release Form lists the necessary steps to secure a car at the terminal, and provides a record of any problems encountered during securement.
Hazardous Material Documentation
Proper documentation of the hazardous materials is critical to safe transport and regulatory compliance. This is also one of the most common causes of error. If the hazardous material is involved in a spill or leak, proper documentation and description will give responders the information needed to resolve the situation safely. If this information isn’t correct, the hazardous materials or fumes can seriously harm workers or the environment.
The hazardous material shipping description will accompany the materials across railways and terminals. It is the shipper’s responsibility to fill out this information properly and completely. The HMR does not require a specific form, but does require that this information be listed on the shipping papers in a specific order. Though there is not a designated form, it is useful to have one form for your hazardous materials, so there is no confusion.
The acronym ISHP is useful for remembering this order:
- Identification number
- Shipping name
- Hazard class
- Packing group
Detailed procedures and training for shipping hazardous materials help to ensure that your shipment makes it to its destination on time and without incident. If you have questions about safety procedures or transportation between terminals, RSI can help. Give us a call or send us a message for more information.



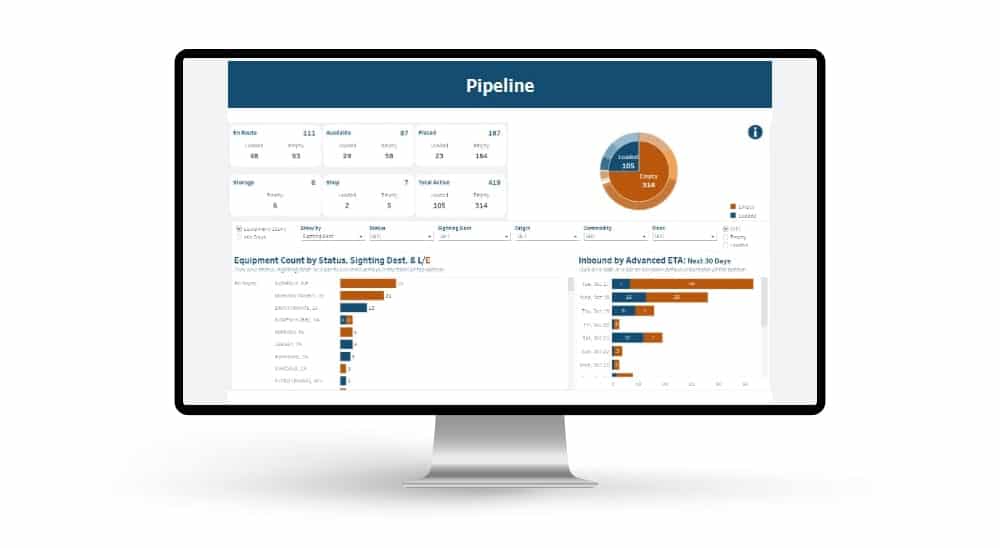 Automated exception reporting of the railcar tracking data makes it easy to identify and troubleshoot jeopardized shipments, thereby enabling you to provide better service to your stakeholders.
Automated exception reporting of the railcar tracking data makes it easy to identify and troubleshoot jeopardized shipments, thereby enabling you to provide better service to your stakeholders.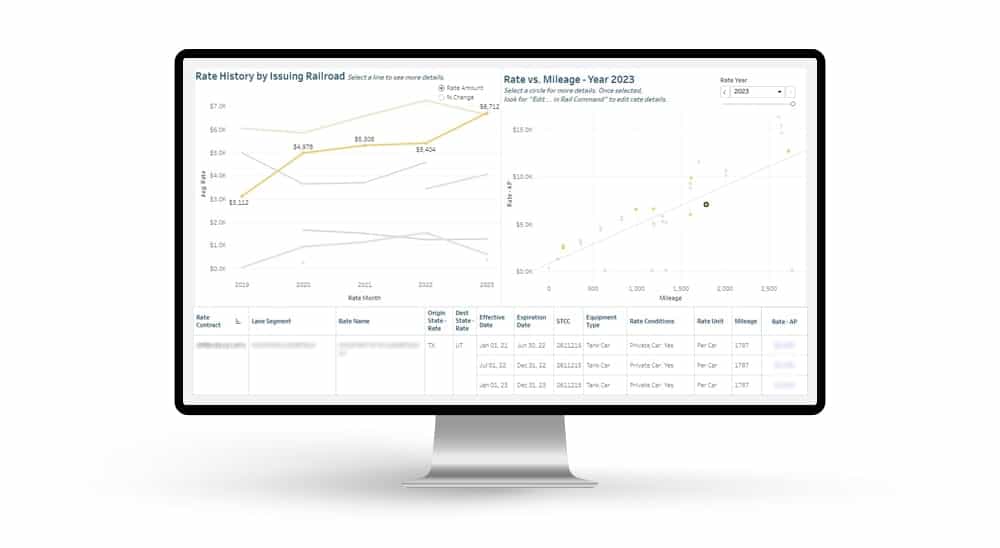 Receive notification of pending rate expirations. Tariff changes and fuel surcharges can be automatically updated.
Receive notification of pending rate expirations. Tariff changes and fuel surcharges can be automatically updated.